
Prerequisites
To follow this guide, you need:- A Snowflake account with access to the target tables.
- Permissions to create users and roles in your Snowflake account.
- An Openlayer project with monitoring mode enabled.
Setup Guide
Step 1: Create a warehouse on your Snowflake account
Navigate to your Snowflake account an create a new warehouse. You will use the warehouse name in the next steps.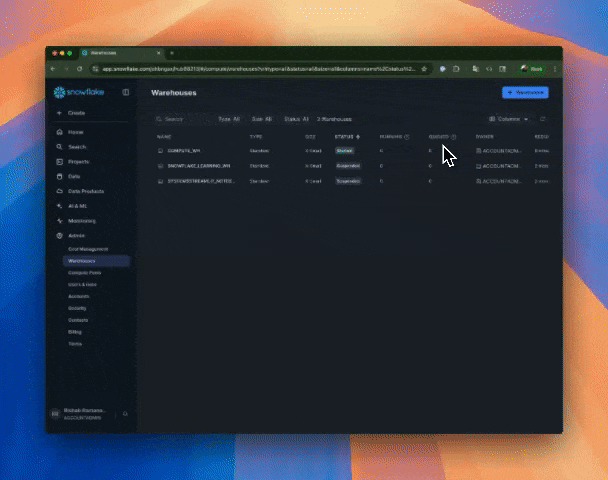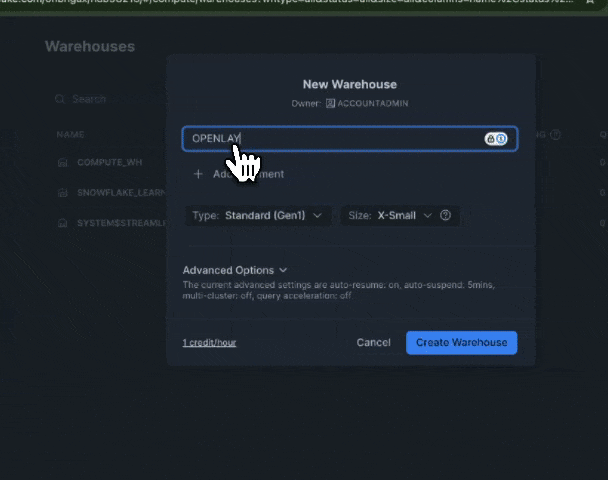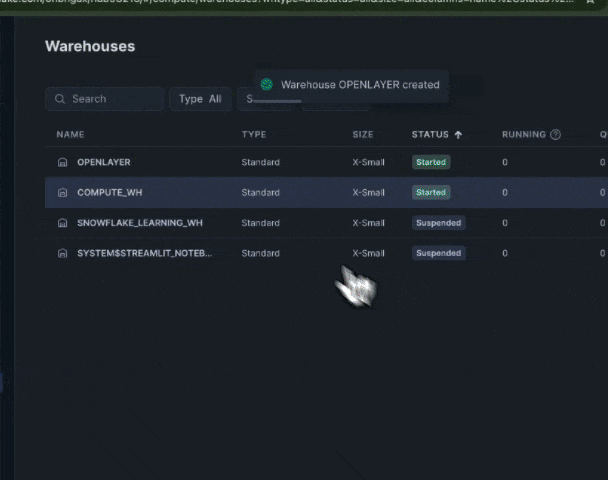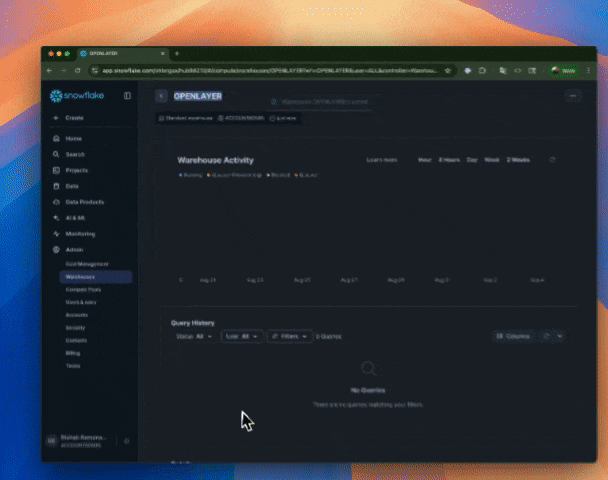 A warehouse is an on-demand, scalable compute cluster used for executing
data processing tasks. Openlayer will connect to a warehouse to
run queries and sync data from the tables you want to monitor.
A warehouse is an on-demand, scalable compute cluster used for executing
data processing tasks. Openlayer will connect to a warehouse to
run queries and sync data from the tables you want to monitor.
Step 2: Create a dedicated user and role
Next, in Snowflake, create a service user and role. They will be used to run queries securely. To do it, run the following commands in a SQL worksheet, replacing placeholders:Replace
[OPENLAYER_PUBLIC_KEY_HERE] in the script below with the public RSA
key available in the Openlayer UI when creating a Snowflake connection.
Step 3: Grant role permissions
The role you created in Step 2 (default toOPENLAYER_FILE_IMPORTER_ROLE) must
have USAGE rights on the warehouse, database, and schema, and SELECT rights on the target tables.
To do it, run the following commands in a SQL worksheet, replacing placeholders:
If you want to connect Openlayer to
views, you need
to grant
SELECT rights on them too. To do it, replace table_name with
view_name in the script above.Step 4: Connect inside Openlayer
In your Openlayer workspace:- Go to Data sources and select Snowflake.
- Click Connect.
- Fill in the fields:
- Snowflake user: the Snowflake username (default to
OPENLAYER_FILE_IMPORTER) - Snowflake role: the role with permissions (default to
OPENLAYER_FILE_IMPORTER_ROLE) - Snowflake account: your account identifier (e.g.
ABCDEFG-XYZ123) - Snowflake warehouse: the warehouse to run queries (the one you created in Step 1)
- Name: a descriptive name for this connection

Step 5: Configure your table
After the connection is created, select the table to monitor:- Database: name of the database
- Schema: schema containing the table
- Table: table name
- Timestamp column: column used to order/filter data for monitoring windows
- Unique id column: column used to identify unique rows for monitoring windows (recommended)
- Data source name: a descriptive name in Openlayer
Optional: ML-specific settings
If the table contains ML outputs, you can provide additional context:- Class names
- Feature names
- Categorical feature names
Troubleshooting
- Permission errors → verify your role has
USAGEon the database/schema/warehouse andSELECTon the table. - Key errors → check that your public key is registered to the Snowflake user and that you are providing the correct private key.
- Empty results → confirm the timestamp column is populated and the right table is selected.

